Introduction
Despite being steadfast about oral care and hygiene, you’ll surely end up experiencing a toothache pain at some stage of your life. Though a decaying tooth or cavity is more often behind the discomfiture resulting from your toothache, there could be numerous other underlying causes of toothache. Other probable toothache causes include:
- Improper or damaged filling
- Pyorrhea
- Gingivitis
- Bruxism (grinding tooth)
- Wisdom teeth emergence
- Fractured tooth
- Abscessed tooth
- Sinusitis
- And so on…
Sometimes a toothache may recede without your having to take a painkiller or other medications and you can prevent its recurrence by following a proper oral care regimen. However, if the toothache persists or becomes severe with every passing moment, calling up a dentist for telephonic consultation and/or making an appointment would be the most practical course of action. The dentist is the appropriate medical professional who can tell you how to stop a toothache by pinpointing the exact cause of your toothache through standardized dental exams or checkups, and suggest a systematic course of treatment (1).
Toothache causes and symptoms (toothache after filling, toothache after root canal)
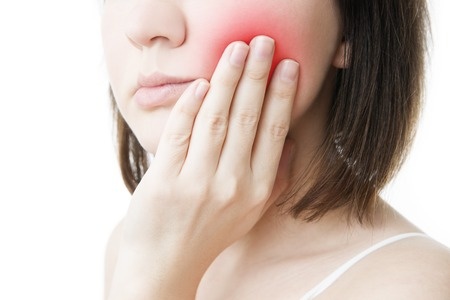
Inflammation in the middle of the tooth known as the pulp can give you a toothache. Nerve axons in the pulp are highly sensitive or susceptible to pain resulting from inflammation in the pulp that can happen because of gum infection, tooth decay, cavity or trauma. Pain in the tooth or jaw is practically widespread nowadays. So, there is no need to be unnecessarily alarmed if you have a shooting pain in your tooth after sipping a chilled beverage or cup of hot tea.
Nevertheless if it continues to ache and lasts for an inordinately long period, say a couple of days, then it could be indicative of a serious underlying issue. Acute dental inflammation will cause pain that may become intolerable and spread to the gums, jaws, and ears (2). Toothache causes could be suggestive of serious ailments like heart disease or diabetes or could be indicate a relatively innocuous tooth fracture or decay. Experiencing toothache after filling or crown gets damaged or toothache after root canal treatment (in case the procedure was hastily completed or not carried out properly) is not uncommon either.
Symptoms or signs leading to toothaches that might warrant medical intervention include:
- Pain while biting into food and chewing
- Inflammation around a tooth or swelling of the cheek or jaw
- Bleeding from the tooth or gums or discharge that has a foul taste or smell
- Recurring spells of fever
- Trauma resulting from infection or injury to the affected area
- Periodontal disease
Sometimes, aches in the jaws or face could be mistaken for a toothache. Pain arising out of sinusitis, otitis (external, middle or internal), laryngitis, and pharyngitis could be misinterpreted as toothache. Injury or wound in the TMJ or temporomandibular joint (the part or section that joins the jaws with the cranium) could also cause pains or aches that many individual confuse with toothaches (3).
Toothache medicines (toothache pain relief)
You may not always be able to schedule an appointment with the dentist right away. In such a circumstance, not attending or treating your pain could intensify the ache leading to a more critical situation. Till the time you arrange a meeting with the dentist, you could abide by some self-treatment techniques for getting relief from inflammation or alleviating pain at least temporarily.
- Use a good quality dental floss to dislodge or remove food particles or condiments that may get trapped in between teeth
- Add a pinch of salt to lukewarm water and thoroughly rinse your mouth with the solution
- If you’re in a trauma owing to an infection or injury in the gums or teeth, you could compress an ice pack on the exterior for getting some relief from pain
- Directly apply clove oil to the affected area with a swab of cotton for numbing the pain (3)
- Direct application of an antiseptic cream or ointment (infused with benzocaine) may also prove effective
- Take toothache medicines like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or a painkiller/analgesic (ibuprofen) when the pain becomes intense
- Abstain from applying topical preparations of aspirin or other analgesics over the gums or teeth to prevent burning or charring
Seeking Medical Care

Calling up a dentist or a GP becomes imperative for seeking his or her counsel for the below-mentioned concerns:
- When self-care treatment procedures don’t offer you relief from toothache
- Going for a thorough dental examination or checkup would still be beneficial even if your ache is relieved as knowing the exact cause will let you cope with and treat the pain more effectively during recurrences
- When you’re down with a fever or putting up with a swelling or having a discharge, it could signal that you’re suffering from an infection of the jawbone, gums or the teeth
- Inflammation or swelling could suggest an abscessed tooth that can be treated via antibiotics or through a surgical process (root canal treatment)
- When you continue to have pain even after extracting a decayed tooth which means your tooth socket or opening has not healed up sufficiently
- Growth or appearance of wisdom teeth in children could be painful. Emergence of wisdom molars cause inflammation or swelling in the area surrounding the tooth could result in infection of the gum as well
- Oftentimes the actual or original cause of your tooth pain may not have anything to do with your teeth, gums or dentine structure. What you may consider as a harmless jaw pain or toothache could be a symptom of heart disease, diabetes, myocardial infarction or ischemia (2)
Toothache home remedies

You know you’ve a toothache when you’re inconvenienced with a sore mouth, throbbing gums, and pounding head. In case you’re not able to fix an engagement with a dentist or doctor right away, you can make the most of toothache home remedies so as to get interim relief (4). Rinsing your mouth with warm salted water is a time-honored home remedy that can be extremely effective in helping you to get relief almost instantly. Other home remedies include OTC pain relievers, cold compress, and oil of clove.
References:
- http://www.emedicinehealth.com
- https://www.deltadentalins.com
- http://www.webmd.com
- http://www.webmd.com

