What is HIV and AIDS?
HIV is a commonly heard word these days. However, it is very important to understand what is HIV and what is AIDS. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the disease which is caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). This virus attacks the CD4 cells commonly called as T cells which are a part of our body’s immune system. The defense mechanism provides immunity and performs the major function of protecting the body from infections by fighting off the bacteria and viruses. This immune system gradually gets affected and the person becomes susceptible to even minor infections. The immunity level of the affected individual decreases further as the disease progresses.
Transmission of HIV
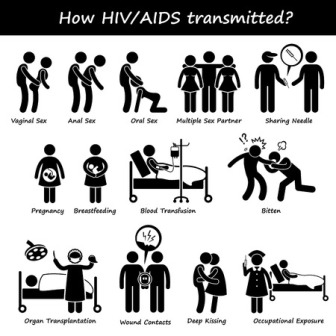
The HIV Virus is found in the body fluids and blood of the affected person. It is present in blood, semen, vaginal fluid and even breast milk. So the disease is transmitted by blood to blood contact or sexual contact.
- Pregnant ladies with HIV infection can pass it on to the unborn baby during delivery or through the breast milk.
- Other common modes of transmission include use of infected needles and syringes which contain blood traces of an infected person.
- Sexual contact in the form of oral sex, vaginal and anal sex
- Through blood transfusion.
- Sharing of infected needles by intravenous drug users.
Symptoms of HIV
AIDS symptoms or HIV symptoms can be better understood if we get an idea about the different stages of the disease.
Stage 1: Acute Infection

After an exposure to the HIV virus, the person is asymptomatic for the first 2-4 weeks which is the incubation period. At this stage, the person is highly infectious but unaware of the disease. He experiences mild flu like symptoms as follows which may continue over a few weeks.
- Fever
- Chills
- Joint pain
- Sore throat
- Night sweats
- Tiredness and weakness
- Skin rashes (HIV Rash)
Stage 2: Asymptomatic Infection
After the initial symptoms regress, there is a stage of clinical latency where the virus continues to grow and multiply but since there are no symptoms, the person feels normal. However he is highly contagious. If no treatment is given, this stage can last up to a decade which will end into a fully blown picture of AIDS.
If the diagnosis is made in time and the person is put on ART, then this stage can be prolonged for a few decades. But AIDS is a lifelong disease as there is no cure for HIV. The person has to live with it till the end.
Stage 3: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
A fully blown picture of AIDS is the most severe form of HIV infection. The person diagnosed at this stage will not be able to live for more than 3 years. The immune system is damaged and the person is very susceptible to even minor infections. Common HIV AIDS symptoms seen during this stage are:
- Fever lasting for weeks
- Long standing chronic diarrhea
- Night sweats
- Permanent tiredness
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Weight loss
- White spots on the tongue
Diagnosis and Treatment of HIV
HIV Test: HIV blood test by ELISA is the commonest diagnostic test and is done in case there is a history of exposure. The results of the test may be negative initially and can take up to three months to get a HIV positive result.
CD4 and CD8 count are done to get an idea about the immunity status. Low CD4 count indicates advanced stage of AIDS.
Treatment is mainly done by Anti-Retroviral Drugs (ARTs). The main aim of treatment is to reduce the viral load and maintain a high CD4 count so that the person is immunologically capable of carrying out his day to day activities. HIV patients are however very susceptible to infections, tuberculosis being the commonest one of all other infections.
Scientists are working on developing a HIV vaccine which is challenging as the virus is highly mutable and adapts as soon as HIV antibodies are introduced.
Prevention of HIV

- Use of a condom can prevent the spread of HIV. Unprotected sex puts one at a risk for contracting HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Sharing needles by intravenous drug users also leads to spread of the disease. Awareness in this matter will prove beneficial.
- Medical and paramedical staff should take adequate care by using gloves to avoid contact with contaminated blood and body fluids of patients.
- All pregnant ladies should be screened for HIV as it is transmitted to the unborn child. An effective treatment plan like planned cesarean, bottle feeding etc can help if the mother is found infected.
- Health and sex education to teenagers should be imparted in all schools to make them aware of the disease.

