What is Mouth Herpes?
Mouth herpes is a viral disease resulting in fever blisters or cold sores infecting the mouth and face. Herpes or Herpes simplex Virus is mainly caused by Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) while the other virus of type 2 (HSV-2) causes Genital herpes.
Mouth herpes{also known as oral herpes) primarily affects children of more than 6 months of age or who are aged 1-2 years and it affects adults also. When this virus is inside your mouth it is sometimes confused with a canker sore. It results in painful red fluid-filled blisters or lesions on the tongue, lips, inside of the cheeks, and gums often accompanied with an itchy or burning sensation. Muscle pain and fever can also be suffered at a later stage. If treatment is ignored, a herpes infection inside your mouth can be dangerous.
It goes through three distinct stages before giving any indications of the occurrence of the infection. The three stages are:
- Primary Infection: This is the first stage wherein the contagion reproduces upon entering from the mucous membrane or skin. Typical symptom is the appearance of oral lesions which may not be present initially resulting in an asymptotic infection. In this case due to lack of symptoms one will be unaware of the presence of an infection. The sores usually takes 21 days to form and become visible, then the blisters will persist up to 10 days before beginning to heal.
- Latency: The virus attacks dorsal root ganglion, a mass of nervous tissue in the spine after moving away from the site it infected.
- Recurrence: An outbreak can recur up to 4 to 6 times a year based on the lifestyle of an individual, emotional & physical stresses and the strength of their immune system.
Is mouth herpes contagious?
Many people wonder— is the mouth herpes contagious? The answer to that is a loud YES. Many times they are viewed as common occurences and not important to your general health. Often parents will simply consider them a normal nuisance part of childhood.
If not treated immediately, it has potential spread to other parts of the body. Being highly contagious in nature it gets readily transmitted by sharing utensils, clothes, and toothbrush. Maintaining sexual contact, kissing and touching also leads to the spread of virus. It is likely to spread more when the virus is present with physical outbursts. It is less contagious if the virus is present without any outward physical signs.
Do everything possible to prevent spreading it to other people. The virus cannot live long when it is not in contact with the skin, so door handles and towels are not likely to spread it. Do not share your personal belongings, like toothbrushes and combs. Wash your hands with soap and water often, and immediately if you touch the sores. This is important so as to minimize the chance of getting ocular herpes (herpes infection of the eye) which is a serious infection. Be especially careful around infants because their immune systems may not be fully developed. Little children often express affection with sloppy wet kisses. This is a common way to spread the herpes virus within the family.
Mouth Herpes Symptoms
You may have mouth herpes without showing any symptoms. The incubation period for the virus after initial contact is anywhere from 2-12 days. Once the sores appear they usually last for 7-21 days. The average incubation time is about 4 days in people. After the lesions have dried and healed the virus remains dormant in your nervous system.
The sores can be very painful, and unsightly, and can lead to certain common flu like indications. Though the signs of mouth herpes vary from person to person and in different regions, these are some common signs:
- Fever
- Muscle ache
- Burning or tingling sensation
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Depression
Because of the aforesaid common symptoms of mouth herpes, the disease is easily mistaken for some other type of infection such as canker sores (Aphthous ulcers). These are ulcers in the mucosa of mouth caused by adverse reaction to some bacterium or by allergies and are not a viral infection. However it should be tested for herpes nonetheless. .
Other major symptoms of mouth herpes are:
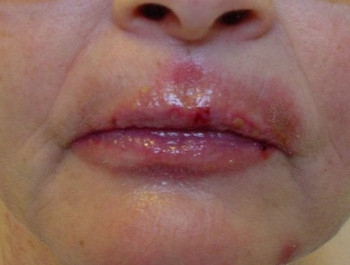
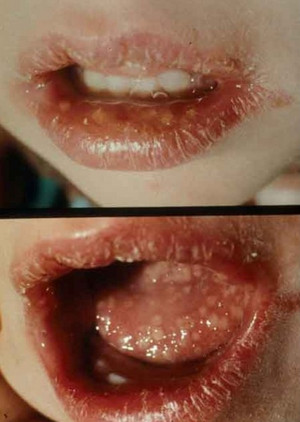
- Sores occur at the frontal portion of tongue, roof of the mouth, lips (herpes labialis), gums, inside of cheeks, gingiva and palates.
- It may be extended outside of the mouth to throat, nose and chin and cause the gums to bleed.
- Swollen lymph nodes of the lower neck (Pharyngitis and Gingivostomatitis) accompanied with fever.
- HSV-1 of pharynx leads to ulcerative fluid filled blisters of the tonsils or lower pharynx.
- The pain can be intense and make it hard to swallow, eat or drink.
- Superficial abscesses of grayish coating may appear on tonsils of people who are above 20 years of age.
- In severe conditions HSV-1 can spread up to other parts of body like eyes (Herpes keratitis), hands (Herpes whitlow) and even the central nervous system (Herpes encephalitis).
- This is autoinoculation which occurs at the time of primary infection if the body’s antibodies fail to render the virus dormant and it spreads out further.
- Herpes keratitis can cause white burning sores on the eye lids and on the surface of cornea.
- Herpes whitlow renders painful abscesses on fingers, thumbs, toes and nails.
Your skin becomes sensitive and may begin to itch or tingle prior to the eruption of lesions . This time is referred to as “prodrome”. Gradually the lesions transform into blisters which ulcerate and crust over and can be extremely painful.
The most common site of occurrence is lips leading to Herpes labialis. The fluid in these sores is highly contaminated and contributes to spreading whtn the tender skin surface breaks open. Upon secretion red sensitive skin is left behind.
When to see a doctor?
Go see the doctor when you notice the early signs of mouth herpes Though the sores will disappear by themselves in 2 to 3 weeks without the help of any treatment measures, it is advisable to consult a doctor if certain conditions accompany the sores:
- Recently you have suffered from some severe health condition that has given you a weakened immune system.
- The cold sores persist and are not showing any signs of healing even after 21 days.
- Frequency of recurrence is high
- You are experiencing irritation in your hands, throat, eyes and neck.
Mouth Herpes Pictures
Picture 1 : Herpes simplex lesion of lower lip (cold sore)
Picture 2 : Herpes Simplex Virus Infection (mouth)
Picture 3 : Mouth Herpes sores
Mouth Herpes Treatment
The basic treatment for mouth herpes is classified in two groups:
One is aimed at alleviating the symptoms and is termed as non-specific treatment while the other type is anti-viral therapies whose primary objective is to speed up the therapeutic process and prevent its relapse. Remedies and cures should be taken seriously in order to get rid of mouth herpes.
Non-specific therapy
- Lesions should be kept clean and dry.
- Witch hazel solution, over the counter, dabbed on lesions will help them dry more quickly.
- Refrain from touching them often, wash your hands immediately.
- Refrain from sharing utensils, cloths, toothbrushes, kissing, hugging, handshakes and sexual contact.
- Any over the counter astringent namely campho-phenique or orabase which contains phenol can be used over the lesions to avoid painful bursting of the blisters later on.
- Eat an insipid diet in order to avoid any irritation to the sores.
Anti-viral therapy
- Recently formulated medicines such as valacyclovir (Valtrex), Oral acyclovir (Zovirax) are recommended to minimize the frequency at which cold sores recur. If taken before the attack of infection in form of pills it will inhibit the HSV-1 reproduction.
- The duration of presence of the eruptions can be potentially reduced with application of topical antiviral ointments like acyclovir (Zovirax) or penciclovir (Denavir) on the affected areas.
- Patient should apply penciclovir immediately within an hour of the occurrence of first signs of symptoms to possibly lessen the pain and prevent viral flaking. Application should be repeated at a rate of every two hours continuously for four days. Acyclovir cream can be utilized for the same purpose upon the first sign of itching.
- The only FDA approved cream, Docosanol (Abreva) is to be applied at a rate of 5 times in a single day starting with the first signs of pain. Its benefits are yet to be established.
Homeopathic medicines can also be used to avoid any adverse effects of allopathic drugs and assist the body’s own healing mechanism. They are approved by FDA and are custom made by the medic in the right proportion to provide immediate relief. One such complete natural product is Herpeset which is to be sprayed on the affected areas especially the tongue. The natural components are quickly absorbed in the blood stream.
Mouth Herpes Home remedies
- Maintain hygiene as discussed above
- Fingernails should be clipped regularly and kept clean
- Drink lots of water
- Apply a good sunscreen to avoid reocurrence of HSV-1. Cover up exposed parts while moving out.
- Apply ice packs on the affected areas as it tends to reduce pain
- Aspirin and Nuprin are some over the counter drugs that can be taken to reduce fever and inflammation. However aspirin is not to be given to children. They can be administered acetaminophen.
- Some consider pressing a warm tea bag over the lesions for about 30 minutes is beneficial.
- Applying common salt, lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) or aloe vera gel speeds up the recovery.
- Eat foods which are rich in lysine, an essential amino acid which produces disease fighting antibodies. It has been valuable in fighting against cold sores.
- Consuming about 1000 mg of lysine in a single day will reduce the duration of lesions
- Prunella Vulgaris, a self heal herb is beneficial in both HSV-1 and HSV-2.
References:
- http://www.webmd.com/genital-herpes/pain-management-herpes
- http://www.emedicinehealth.com/oral_herpes/page3_em.htm
- http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cold-sore/DS00358
- http://www.medicinenet.com/herpes_simplex_infections_non-genital/page4.htm


By taking lysine daily I am able to avoid most outbreaks. Wearing a hat when out of doors helps. I have had this problem most of my life I am 78 year old female.