About Hepatitis
Hepatitis is basically the inflammation of the liver. It can be acute or chronic in nature and the commonest causative organisms are viruses. The main function of the liver in our body is production of bile to aid the process of digestion. It helps in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. It is responsible for the excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones and drugs. Plasma proteins like albumin and clotting factors of the blood are synthesized in the liver. Viral hepatitis is classified into the following types Hepatitis A, B,C, D and E.
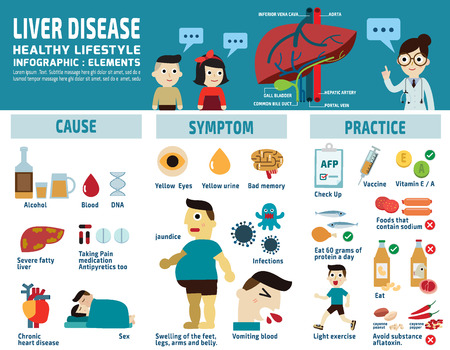
Causes of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E are generally caused by consuming contaminated water or eating contaminated food, where as Hepatitis B, C and D occur due to contact with contaminated blood and other body fluids. Hepatitis B and C are chronic forms of infection and the person remains a carrier and can pass on the disease to other through blood and body fluids like saliva, breastmilk, vaginal secretions etc.
The non viral causes of hepatitis are alcoholic hepatitis due to excessive alcohol consumption which leads to cirrhosis of liver and autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Hepatitis presents with a wide range of symptoms that could be mild itching to severe liver failure. The following are the symptoms of acute and chronic hepatitis.
- Acute hepatitis: The onset is with a prodromal phase that is characterized by non specific symptoms like fever, malaise, nausea , vomiting, headache etc. Later on symptoms specific to liver disturbances may develop like strong yellow colored urine and clay colored stools. This is followed by yellowish discoloration of the skin and schlera of the eyes. This stage can last up to 4 weeks. The last stage is the recovery phase where the clinical symptoms begin to regress and the laboratory values of liver functions are still high. The liver is also enlarged. Hepatitis A and E are normally acute in nature and resolve fully within 1-2 months. Drug induced hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis also present like with similar symptoms.
- Chronic Hepatitis: If the symptoms of acute hepatitis do not resolve within 6 months, it is termed as chronic hepatitis. Initially there are only non specific symptoms but gradually as the hormone metabolism in the liver gets affected, deeper symptoms come up like hirsutism and amenorrhoea. Long standing liver disease and damage to liver functions ends in cirrhosis of liver and its complications.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis
The presence of the above symptoms or a history of exposure to a contaminated persons blood will need to be investigated. The abdominal examination will reveal an enlarged liver.
The most indicative tests are blood tests called Liver function Tests which give a complete detail of the liver enzymes and proteins. If the levels are elevated, it indicates a deranged liver function. The diagnosis is normally confirmed by an ultrasound of the abdomen and viral markers that detect the presence of antibodies in the blood.
Treatment of Hepatitis
Acute types like hepatitis a and E have an infective aetiology and are usually self limiting ad the symptoms resolve. Symptomatic treatment may be required for the vomiting or diarrhea. Vaccination for Hepatitis A is mostly given to babies between 12 to 18 months and is fairly effective.
Chronic forms of hepatitis like hepatitis b resolve by treatment with antiviral drugs. Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all babies and health care personnel who have a risk of coming in contact with infected blood.
Hepatitis C is a chronic disease and it leads to damage to the liver and cirrhosis. Severe cases may need a hepatitis c liver transplant.
Hepatitis D is usually treated with a medicine called alpha interferon.
Hepatitis and Pregnancy
Acute viral hepatitis is a very common cause of jaundice during pregnancy and is commonly caused by intake of contaminated food and water. Jaundice is an indicator of liver disease but the type of hepatitis cannot be assessed clinically. Detailed tests may be required to isolate the type of hepatitis. The most useful tests here are the SGOT, SGPT levels. High levels of SGPT during pregnancy can be harmful to the fetus.
Hepatitis B can pass on to the unborn fetus via the blood so all pregnant women are routinely screened for hepatitis and AIDS. If a pregnant women is found to be positive, systematic vaccinations can help to protect the baby.
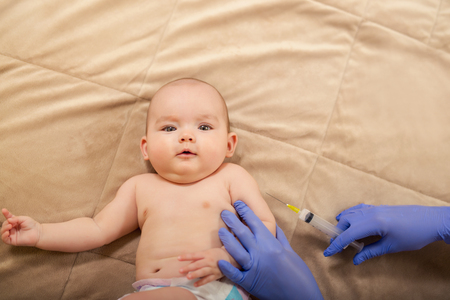
Hepatitis Vaccination in Infants
Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended between 12 to 18 months of age. A booster dose is given 6-18 months after the first dose.
Hepatitis B vaccine is given to babies in the first few days after birth. The first dose is given when they are still in the hospital. There are total four doses and the gap will depend on the type of the vaccine used. Children get the first dose in the first week and complete all four doses by the age of six months. The second dose is given around 1-2 months of age and the third one at six months.