Birth control is also commonly known as fertility control or contraception. This is basically a method to prevent pregnancy and to attain a proper spacing between two children. In recent times, it has gained much popularity as couples now plan the pregnancy and so it is also termed as family planning. There are many family planning methods ranging from emergency birth control pills to permanent solutions like sterilization surgery.
Methods of Contraception
There are many effective birth control options available these days. Here we shall discuss few of them in details:
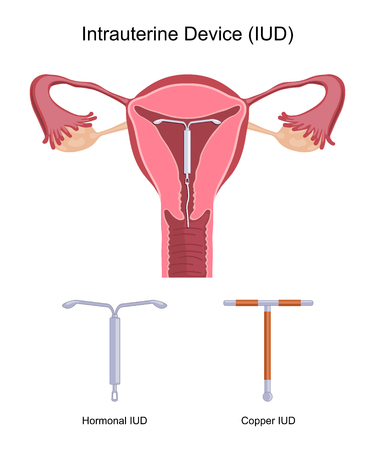
- IUDs-IntraUterine Devices: IUDs are small intrauterine devices that are impregnated with hormones. They are commonly known as copper T or copper iud. It is a T shaped device that is inserted into the uterine cavity. The mode of action of the IUD is that it elutes hormones or copper that make the cervical mucous thick thus preventing fertilization. It also prevents ovulation and stops uterine wall build up. The most effective kind of IUD is the levonorgestrel (progesterone) releasing intrauterine device. It provides contraception for a period of five years. An iud is recommended for those women who have already had their first child. Common iud side effects include spotting and cramping pain the abdomen. The efficacy rate is known to be 99%.
- Barrier Methods: Barrier methods of contraception are those devices that physically prevent the entry of the sperm into the uterine cavity and thereby preventing fertilization and pregnancy. These include male and female condoms, cervical caps and diaphragms and contraceptive sponges with spermicide. This is the commonest over the counter birth control option.Condoms are the most popular and effective barrier method. They are commonly made out of latex, are easy to use and inexpensive. This method involves putting on a condom over the erect penis of the male. This prevents the entry of the sperms into the cervix of the female partner and thereby prevents the female from conceiving. Another very important use of the condom is that it prevents the transmission of sexually transmitted disease in individuals having unprotected sex or having illicit sexual relations. The commonest mode of transmission of HIV/AIDS and other STDs like syphilis and gonorrhea is via sexual intercourse. There is a small failure rate associated with condoms due to improper usage or tearing of the condom but it accounts for a very small percentage of cases.
- Hormonal Methods and Contraceptive Pills: There are two types of contraceptive pills. One is the estrogen progesterone pill and the other is the only progesterone pill also called as mini pill. Both these provide contraception by preventing ovulation and thickening up the cerival mucus. In turn both these will prevent the egg and sperm from fertilizing and thereby the chances of a pregnancy become zero.The pill is often associated with side effects like breast tenderness, headache and nausea due to the effect of hormone estrogen.Other hormonal methods are contraceptive implants under the skin, birth control patch and injections. The commonest injection (birth control shot) used is depo provera which provides contraception for a period of one year.
- Sterilization Surgery: Surgical sterilization is method of providing permanent contraception. It is available as vasectomy or male birth control and tubal ligation in females. In males, the vas deference that carries the sperms is ligated and in females the fallopian tubes that transport the egg to the uterine cavity is ligated. In both the cases, there is a creation of a mechanical block due to which the egg and sperm cannot meet and thereby the chance of a pregnancy is ruled out. This option is suitable for those females who already have two or more children above the age of 5. Although it is a permanent surgical procedure, if needed surgical re-canalization can be done. This mode of birth control does not provide any protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
- Emergency Contraception: Emergency contraceptive pills are used mostly after an episode of unprotected sex with a hope of preventing a pregnancy. They are also referred to as the morning after pill. The mode of action of these pills is to prevent ovulation and fertilization. They do not provide any protection against sexually transmitted diseases. The various options include high dose contraceptive pills, ulipristal which has been found to be more effective in obese subjects, levonogestrel, mifeprestone and IUDs.
- Breastfeeding : A breastfeeding mother usually has lactational amenorrhoea for the first six months. This period is known to be a natural contraceptive. The two pre-conditions here are absence of periods and exclusive breast feeding of the baby. This is not an absolute contraceptive period and in many females, fertility returns early and they can conceive even when they are breast feeding.

Advantages of Using Birth Control
Birth control has multiple benefits. It provides freedom to the couple to have a normal sex life without the fear of pregnancy. There are a multitude of options available and the couple can choose what suits them the best. Contraception helps to space the children adequately and also provide the mother time to recuperate from the first pregnancy. Children born very close in age gap, make it very difficult for the mother as her body barely gets any time to recover from the strain of the first pregnancy. This was one major reason behind high infant mortality rates in some Asian countries. Barrier methods provide protection against sexually transmitted diseases. The awareness of STDs in today’s youth is very important as it can prevent unwanted teen pregnancies and transmission of HIV/AIDS.